ETF
Introduction :
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) represent a popular and innovative investment vehicle that has gained widespread acceptance among investors globally. Introduced in the early 1990s, ETFs have revolutionized the way investors access financial markets, offering a diverse array of benefits and opportunities.
What is ETF :
An Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF) is popular among Indian investors as it combines the benefits of both mutual funds and stocks. It operates as a collection of stocks or other securities, traded on stock exchanges like individual stocks. ETFs track various indices, commodities, bonds, or baskets of securities, offering investors a convenient way to gain exposure to diversified portfolios through a single investment vehicle.
Types of ETFs :
There are two types of ETF below,
- NSE ETFs(National stock exchange)
- BSE ETFs(Bombay stock Exchange)
NSE ETF :
The National Stock Exchange (NSE) was established in 1992, with its headquarters located in Mumbai. The NSE’s benchmark index is the NIFTY 50. The NSE four types of ETFs.
-
Equity ETFs :
These ETFs invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks listed on the National Stock Exchange (NSE), tracking indices like the NIFTY 50. By mirroring the performance of these indices, investors gain exposure to a broad range of companies across different sectors, enhancing portfolio diversification and potentially reducing risk.
-
Gold ETFs :
-
Debt ETFs :
These ETFs invest in a portfolio of fixed-income securities such as government bonds, corporate bonds, or money market instruments.
-
World Indices ETFs :
These ETFs provide exposure to global stock markets by tracking indices of major international exchanges.
BSE ETF :
The Bombay Stock Exchange(BSE) was established in 1875, with its also located in Mumbai, The BSE’s benchmark index is the SENSEX. The BSE three types of ETSs.
-
Equity ETFs :
Similar to NSE Equity ETFs, these funds invest in a basket of stocks listed on the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE), tracking indices like the SENSEX.
-
Gold ETFS :
These ETFs invest in gold, mirroring the price movements of physical gold, but they are listed on the Bombay Stock Exchange.
-
Liquid ETFs :
These ETFs invest in highly liquid short-term instruments such as treasury bills, commercial paper, and certificates of deposit, providing investors with a low-risk avenue for short-term investments.
ETFs Advantages :
- The ETFs is a Next Level of Mutual Fund.
- Diversified Portfolio :A diversified portfolio within an ETF typically includes various types of stocks across different sectors and industries.
- Easier trading. – buy & sell.
- Simplicity & Low cost.
- Low Expense Ratio :ETFs generally have lower expense ratios compared to mutual funds, making them more cost- effective investment options for investors seeking to minimize fees and expenses.
- Low investment amounts.
Eg : If you want to buy all the stocks in the Nifty 50 index, you would need a significantly higher amount, typically exceeding 1 lakh rupees. However, by investing in an ETF like ICICINIFTY, which tracks the Nifty 50 index, you can achieve exposure to all the Nifty 50 stocks with a much lower investment amount. For instance, if the price of ICICINIFTY ETF is 142 rupees, you can gain proportional exposure to the Nifty 50 index by purchasing shares of this ETF at a fraction of the cost required to buy all the individual stocks.
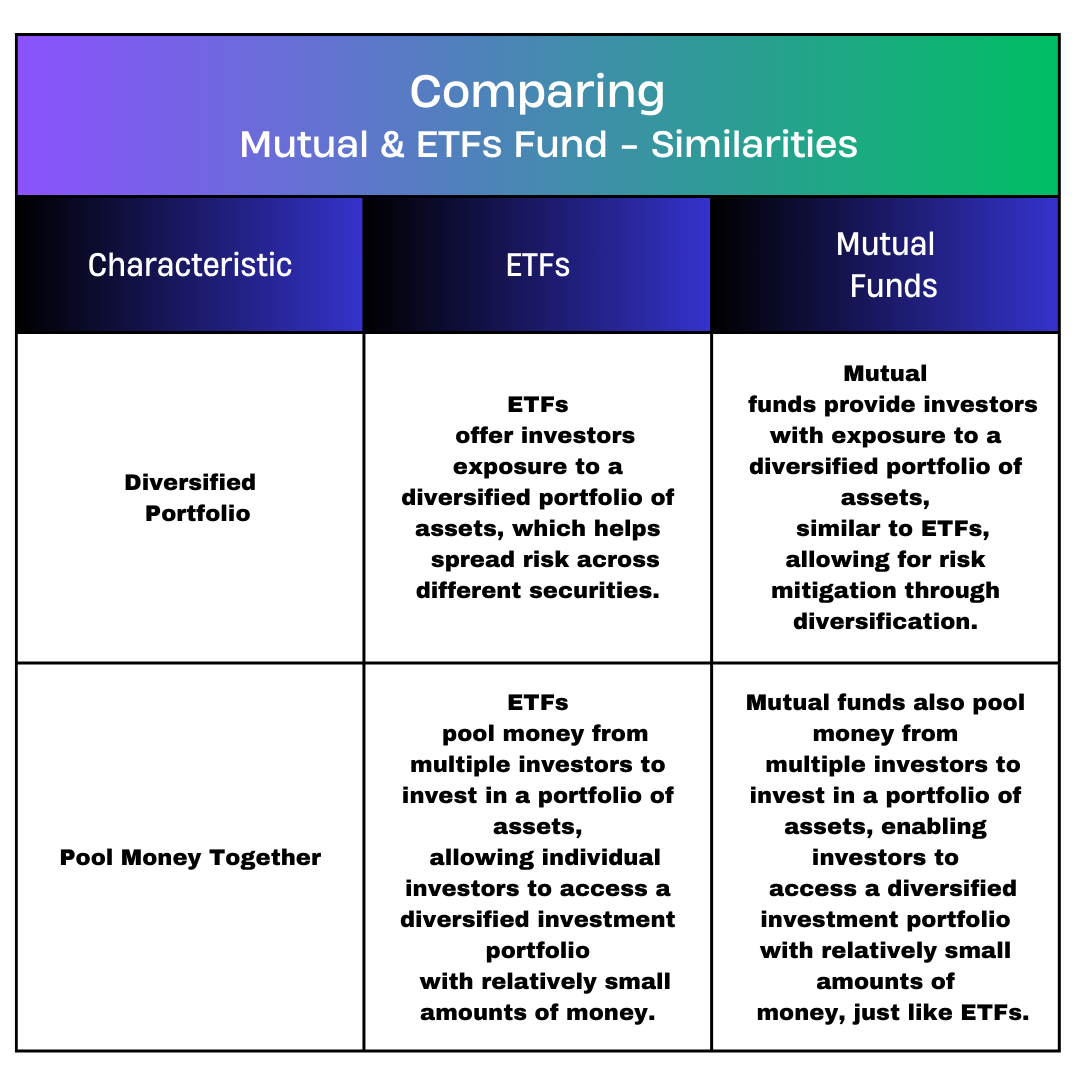
Comparing Mutual Funds :
Similarities :
- Diversified Portfolio
- Pool Money together.
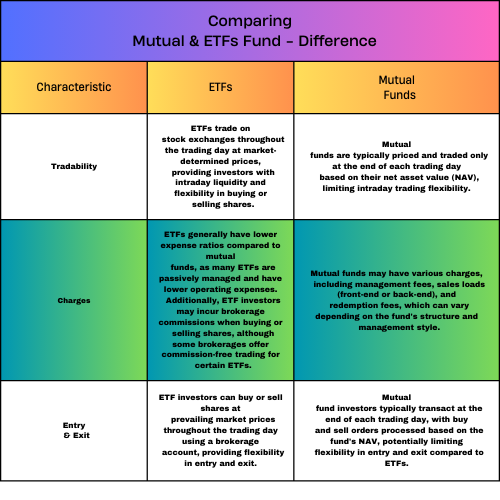
Difference :
- Tradability
- Charges
- Entry & exit
Function of ETFs :
When the demand for ETFs rises, the value of the ETF is not solely determined by market demand but is also based on its net asset value (NAV). Asset management companies, already pre-appointed authorized participants, ensure liquidity by automatically supplying ETFs to meet demand. For example, in the case of a high demand for Nifty 50 ETF, these companies collect stocks from the Nifty 50 index to match the demand. This process ensures that ETFs remain liquid and their value closely tracks their NAV. For instance, ICICINIFTY ETF, with a NAV of 142 rupees, is based on its traded value, which increases or decreases in response to market demand. The ETF’s benchmark is the NIFTY 50 Index.
- Authorized participants
- Stock Market
- Broker.
How to Buy :
The ETF buy step by step detail in below,
Open Your Trading Terminal:
Log in to your brokerage account and open your trading terminal or platform.
Search for the ETF:
Use the search function or navigate to the appropriate section to find the ETF you want to buy. In this example, let’s use ICICINIFTY as the ETF.
Navigate to NSE (National Stock Exchange):
Since ICICINIFTY is listed on the National Stock Exchange (NSE), make sure you’re on the NSE platform within your trading terminal.
Select ICICINIFTY:
Once you’re on the NSE platform, search for ICICINIFTY by typing its name or ticker symbol into the search bar. Click on the ETF to view its details.
Place an Order:
After selecting ICICINIFTY, you’ll have the option to place a buy or sell order. Click on the appropriate button to initiate the order.
Specify Order Details:
Enter the quantity of ICICINIFTY shares you want to buy and select the order type (e.g., market order, limit order). You may also set any additional parameters such as validity and order conditions.
Review and Confirm:
Review the order details to ensure accuracy. Double-check the quantity, order type, and any other relevant information. Once you’re satisfied, confirm the order to execute the trade.
Monitor Your Investment:
After executing the order, monitor your investment in ICICINIFTY regularly to track its performance. You can use the trading terminal’s portfolio tracking tools or external financial resources for monitoring.
Consider Rebalancing:
Periodically review your investment portfolio and consider rebalancing if necessary. Rebalancing may involve buying or selling ICICINIFTY shares to realign with your target asset allocation.
Understand Fees and Expenses:
Be aware of any fees and expenses associated with buying and holding ICICINIFTY, including brokerage commissions, expense ratios, and potential taxes. Understanding these costs can help you manage your investment expenses effectively.
What is Mutual Funds?